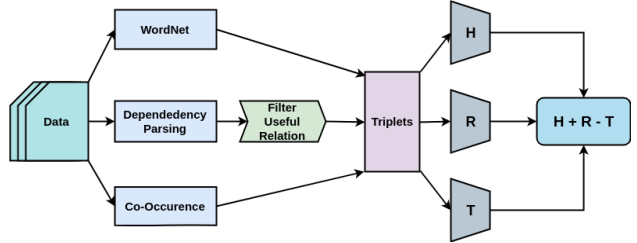
Word embedding techniques in literature are mostly based on Bag of Words models where words that co-occur with each other are considered to be related. However, it is not necessary for similar or related words to occur in the same context window. In this paper, we propose a new approach to combine different types of resources for training word embeddings. The lexical resources used in this work are Dependency Parse Tree and WordNet. Apart from the co-occurrence information, the use of these additional resources helps us in including the semantic and syntactic information from the text in learning the word representations. The learned representations are evaluated on multiple evaluation tasks like Semantic Textual Similarity, Word Similarity. Results of the experimental analyses highlight the usefulness of the proposed methodology.

@inproceedings{10.1145/3342558.3345418,
author = {Dewalkar, Swapnil and Desarkar, Maunendra Sankar},
title = {Multi-Context Information for Word Representation Learning},
year = {2019},
isbn = {9781450368872},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3342558.3345418},
doi = {10.1145/3342558.3345418},
abstract = {Word embedding techniques in literature are mostly based on Bag of Words models where words that co-occur with each other are considered to be related. However, it is not necessary for similar or related words to occur in the same context window. In this paper, we propose a new approach to combine different types of resources for training word embeddings. The lexical resources used in this work are Dependency Parse Tree and WordNet. Apart from the co-occurrence information, the use of these additional resources helps us in including the semantic and syntactic information from the text in learning the word representations. The learned representations are evaluated on multiple evaluation tasks like Semantic Textual Similarity, Word Similarity. Results of the experimental analyses highlight the usefulness of the proposed methodology.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Document Engineering 2019},
articleno = {21},
numpages = {4},
keywords = {Dependency Parsing, Representation Learning, Word embedding, WordNet},
location = {Berlin, Germany},
series = {DocEng '19}
}