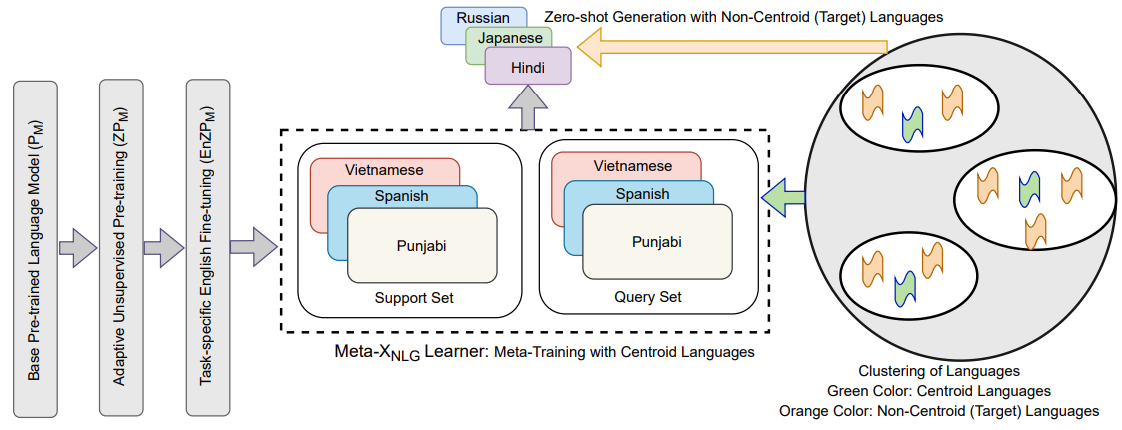
Recently, the NLP community has witnessed a rapid advancement in multilingual and cross-lingual transfer research where the supervision is transferred from high-resource languages (HRLs) to low-resource languages (LRLs). However, the cross-lingual transfer is not uniform across languages, particularly in the zero-shot setting. Towards this goal, one promising research direction is to learn shareable structures across multiple tasks with limited annotated data. The downstream multilingual applications may benefit from such a learning setup as most of the languages across the globe are low-resource and share some structures with other languages. In this paper, we propose a novel meta-learning framework (called Meta-X$_{NLG}$) to learn shareable structures from typologically diverse languages based on meta-learning and language clustering. This is a step towards uniform cross-lingual transfer for unseen languages. We first cluster the languages based on language representations and identify the centroid language of each cluster. Then, a meta-learning algorithm is trained with all centroid languages and evaluated on the other languages in the zero-shot setting. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this modeling on two NLG tasks (Abstractive Text Summarization and Question Generation), 5 popular datasets and 30 typologically diverse languages. Consistent improvements over strong baselines demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed framework. The careful design of the model makes this end-to-end NLG setup less vulnerable to the accidental translation problem, which is a prominent concern in zero-shot cross-lingual NLG tasks.

@inproceedings{maurya-desarkar-2022-meta,
title = {Meta-X$_{NLG}$: A Meta-Learning Approach Based on Language Clustering for Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual Transfer and Generation},
author = {Maurya, Kaushal and
Desarkar, Maunendra},
booktitle = {Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022},
month = may,
year = {2022},
address = {Dublin, Ireland},
publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics},
url = {https://aclanthology.org/2022.findings-acl.24},
doi = {10.18653/v1/2022.findings-acl.24},
pages = {269--284},
abstract = {Recently, the NLP community has witnessed a rapid advancement in multilingual and cross-lingual transfer research where the supervision is transferred from high-resource languages (HRLs) to low-resource languages (LRLs). However, the cross-lingual transfer is not uniform across languages, particularly in the zero-shot setting. Towards this goal, one promising research direction is to learn shareable structures across multiple tasks with limited annotated data. The downstream multilingual applications may benefit from such a learning setup as most of the languages across the globe are low-resource and share some structures with other languages. In this paper, we propose a novel meta-learning framework (called Meta-X$_{NLG}$) to learn shareable structures from typologically diverse languages based on meta-learning and language clustering. This is a step towards uniform cross-lingual transfer for unseen languages. We first cluster the languages based on language representations and identify the centroid language of each cluster. Then, a meta-learning algorithm is trained with all centroid languages and evaluated on the other languages in the zero-shot setting. We demonstrate the effectiveness of this modeling on two NLG tasks (Abstractive Text Summarization and Question Generation), 5 popular datasets and 30 typologically diverse languages. Consistent improvements over strong baselines demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed framework. The careful design of the model makes this end-to-end NLG setup less vulnerable to the accidental translation problem, which is a prominent concern in zero-shot cross-lingual NLG tasks.}
}