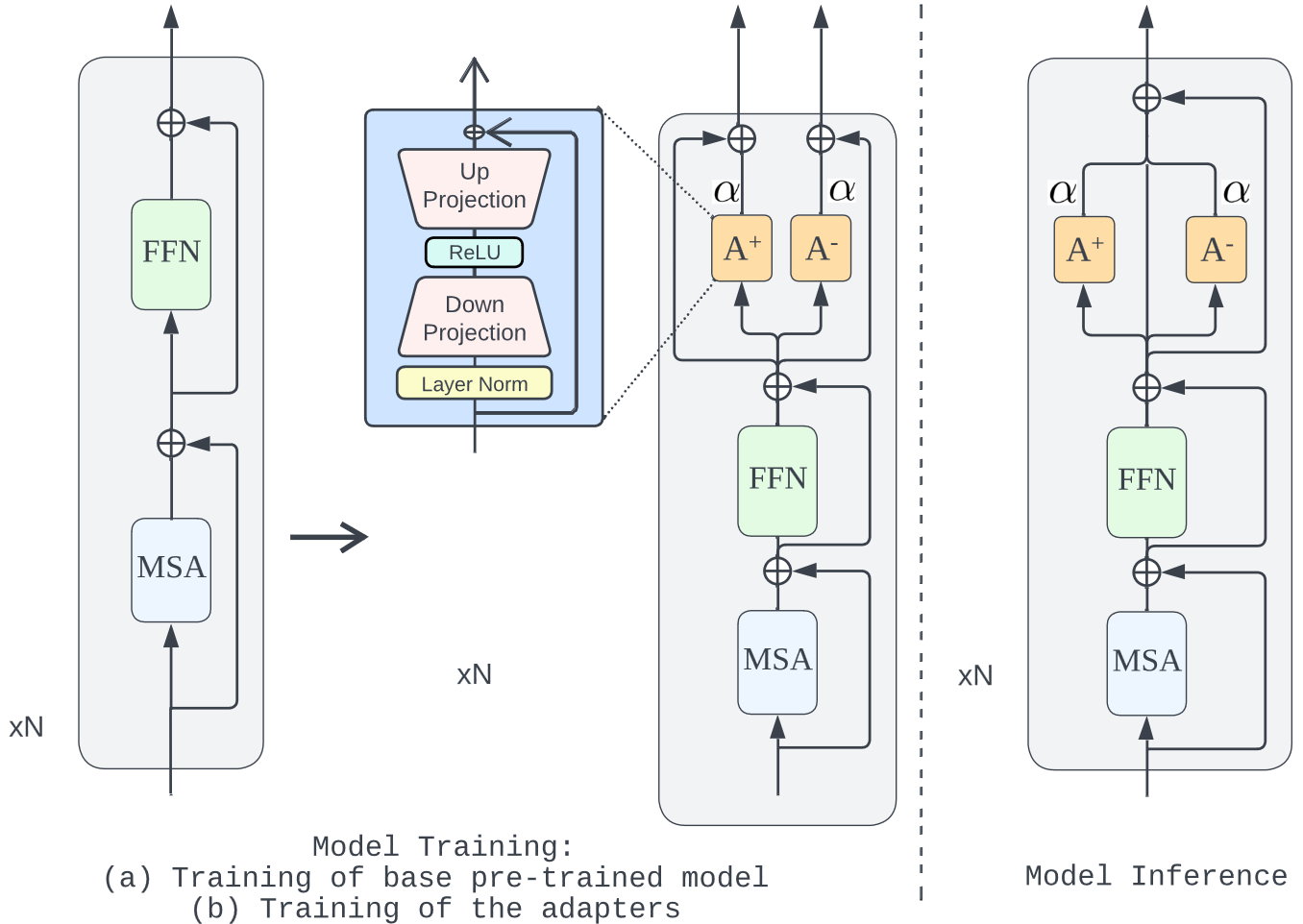
Recent Query Auto-completion (QAC) systems leverage natural language generation or pre-trained language models (PLMs) to demonstrate remarkable performance. However, these systems also suffer from biased and toxic completions. Efforts have been made to address language detoxification within PLMs using controllable text generation (CTG) techniques, involving training with non-toxic data and employing decoding time approaches. As the completions for QAC systems are usually short, these existing CTG methods based on decoding and training are not directly transferable. Towards these concerns, we propose the first public QAC detoxification model, Detoxifying Query Auto-Completion (or DQAC), which utilizes adapters in a CTG framework. DQAC operates on latent representations with no additional overhead. It leverages two adapters for toxic and non-toxic cases. During inference, we fuse these representations in a controlled manner that guides the generation of query completions towards non-toxicity. We evaluate toxicity levels in the generated completions across two real-world datasets using two classifiers: a publicly available (Detoxify) and a search query-specific classifier which we develop (QDetoxify). DQAC consistently outperforms all existing baselines and emerges as a state-of-the-art model providing high quality and low toxicity. We make the code publicly available at https://shorturl.at/zJ024

@inproceedings{10.1007/978-981-97-2266-2_9,
author = {Maheswaran, Aishwarya
and Maurya, Kaushal Kumar
and Gupta, Manish
and Desarkar, Maunendra Sankar},
editor = {Yang, De-Nian
and Xie, Xing
and Tseng, Vincent S.
and Pei, Jian
and Huang, Jen-Wei
and Lin, Jerry Chun-Wei},
title = {DQAC: Detoxifying Query Auto-completion with Adapters},
booktitle = {Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining},
year = {2024},
publisher = {Springer Nature Singapore},
address = {Singapore},
pages = {108--120},
abstract = {Recent Query Auto-completion (QAC) systems leverage natural language generation or pre-trained language models (PLMs) to demonstrate remarkable performance. However, these systems also suffer from biased and toxic completions. Efforts have been made to address language detoxification within PLMs using controllable text generation (CTG) techniques, involving training with non-toxic data and employing decoding time approaches. As the completions for QAC systems are usually short, these existing CTG methods based on decoding and training are not directly transferable. Towards these concerns, we propose the first public QAC detoxification model, Detoxifying Query Auto-Completion (or DQAC), which utilizes adapters in a CTG framework. DQAC operates on latent representations with no additional overhead. It leverages two adapters for toxic and non-toxic cases. During inference, we fuse these representations in a controlled manner that guides the generation of query completions towards non-toxicity. We evaluate toxicity levels in the generated completions across two real-world datasets using two classifiers: a publicly available (Detoxify) and a search query-specific classifier which we develop (QDetoxify). DQAC consistently outperforms all existing baselines and emerges as a state-of-the-art model providing high quality and low toxicity. We make the code publicly available{\$}{\$}^{\{}1{\}}{\$}{\$}1.({\$}{\$}^{\{}1{\}}{\$}{\$}1https://shorturl.at/zJ024)},
isbn = {978-981-97-2266-2}
}